If price is above AVC, however, he can minimize his losses by producing where MC equals MR2. Now suppose that the astrological forecast industry consists of Madame LaFarge and thousands of other firms similar to hers. At the market price, P 1, the firm's profit maximizing quantity is Q 1. Figure 9.7 Applying the Marginal Decision Rule. A top executive in the new firm said that Colussy just found the elimination of the satellites a terrible waste. SRAS might look a lot like a supply curve in a product market, but some key differences make SRAS different than "supply." Because total revenue equals price (P) times quantity (Q), dividing by quantity leaves us with price. Tony Gortari experiences a loss when price drops below ATC, as it does in Panel (b) as a result of a reduction in demand. Because higher inflation leads to more output, higher inflation is also associated with lower unemployment in the short run. First, determine the enterprises profit-maximising output degree when the market cost price is Suppose that his total fixed cost is $400 per month. The equation used to calculate the short-run aggregate supply is: Y = Y + ( P P e). Price also equals average revenue, which is total revenue divided by quantity. That means that if conditions change, like a recession happens, prices will quickly adapt to that change. Posted 3 years ago. You can easily remember all of the shocks that shift SRAS by thinking of. WebThe aggregate supply curve shows the relationship between the price level and the quantity of goods and services supplied in an economy. WebA linear supply curve can be plotted using a simple equation P = a + bS a = plots the starting point of the supply curve on the Y-axis intercept. For one, it represents a short-run relationship between price level and output supplied. The firm's equilibrium supply of 29 units of output is determined by the intersection of the marginal cost and marginal revenue curves (point d in Figure ). Hence, the firm's fixed costs are considered sunk costs and will not have any bearing on whether the firm decides to shut down. Marginal revenue equals the market price. No producer likes a loss (that is, negative economic profit), but the loss solution shown in Figure 9.8 Suffering Economic Losses in the Short Run is the best Mr. Gortari can attain.
When producing 4,444 pounds of radishes per month, Mr. Gortari faces an average total cost of $0.23 per pound. How come on the SRAS graph, a shift to the left or right does not change the real GDP? It is an indicator of the adjustments the economy makes in the event of changes. It is found by extending horizontal lines from the ATC and MR curve to the vertical axis and taking the area of the rectangle formed. It rises at an increasing rate over the range of diminishing marginal returns. In the market model, supply slopes up because of the profit motive of individual firms. In this article, youll get a quick review of the Phillips curve model, including: The Phillips curve illustrates that there is an inverse relationship between unemployment and inflation in the short run, but not the long run. Principles of Economics by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted. WebThe economy is always operating somewhere on the short-run Phillips curve (SRPC) because the SRPC represents different combinations of inflation and unemployment. It is usually an upward-sloping curve as the relationship between price increases is directly proportional to the rise in output levels. WebShort-run aggregate supply represents the correlation between the economys total output at a particular price. The current supply given a firms capital expenditure on fixed assets. If the firm's average variable costs are less than its marginal revenue at the profit maximizing level of output, the firm will not shut down in the shortrun. In making this determination, the firm will take into account its average variable costs rather than its average total costs. Suppose, for example, he decided to operate where marginal cost equals marginal revenue, producing 1,700 pounds of radishes per month. The long-run Phillips curve is vertical at the natural rate of unemployment. The SRAS curve shows the positive relationship between the price level and output. If there is unanticipated inflation, firms benefit from those long-term contracts because they are paying wages (and other resource prices) using dollars that arent worth as much, so the real wages they are paying decrease. The length of the rectangle is 29. As the market price rises, the firm will supply more of its product, in accordance with the law of supply. If he shut down, he would lose only his fixed cost. So the SRAS will shift to the right. Therefore, Mr. Gortari should continue to produce an output at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue. If the market price is less than the minimum average total cost, the firm will still produce; however, it will be making an economic loss. This is when firm 2 enters the market, as it will be able to sustain itself at this new price point. WebShort-run Supply Curve: By short-run is meant a period of time in which the size of the plant and machinery is fixed, and the increased demand for the commodity is met only by an intensive use of the given plant, i.e., by increasing the amount of the variable factors. Building confidence in your accounting skills is easy with CFI courses! WebFig. Thus he would suffer a greater loss by continuing to operate than by shutting down.
Fig. The satellites were the primary communication devices of Iridiums satellite phone system. The case where the firm is incurring shortrun losses but continues to operate is illustrated graphically in Figure (a). Higher inflation will likely pave the way to an expansionary event within the economy. Increasing the price level causes a movement along the short run aggregate supply curve, leading to higher output and higher employment. Explain when a firm will shut down in the short run and when it will operate even if it is incurring economic losses. The firm's losses are given by the area of the shaded rectangle, abed. If this is not the case, the firm may continue its operations in the shortrun, even though it may be experiencing losses. As the market price rises, the firm will supply more of its product, in accordance with the law of supply. Today Iridiums customers include ships at sea (which account for about half of its business), airlines, military uses, and a variety of commercial and humanitarian applications. Adding the quantities supplied by all the other firms in the market, suppose we get a quantity supplied of 280,000. Acmes economic profit per day equals about $126. Here, that occurs at an output of 4,444 pounds of radishes per month. But the total cost curve becomes steeper and steeper as diminishing marginal returns set in. As the market price rises, the firm will supply more of its product, in accordance with the law of supply. In order to produce efficiently, the firm should adjust its fixed costs to a level that minimizes the average total cost of production. The short-run is the time period in which at least one input is fixed generally property, plant, and equipment (PP&E). The hope was that the pieces would burn to bits on their way down through the atmosphere, but there was the chance that a building or a person would take a direct hit. After all, if prices adjust so well, why wasnt the depression going away? Eventually, the total cost and total revenue curves will have the same slope. The firm's average variable cost curve, however, lies below its marginal revenue curve, implying that the firm is able to cover its variable costs. Now suppose that the astrological forecast industry consists of Madame LaFarge and thousands of other firms similar to hers. Often one model is closely related to another model. We assume that the radish market is perfectly competitive; Mr. Gortari runs a perfectly competitive firm. 8 shows that at a price of Rs. The equation for the upward sloping aggregate supply curve, in the short run, is Y = Ynatural + a (P - Pexpected). Mr. Gortari is better off producing where marginal cost equals marginal revenue because at that output price exceeds average variable cost. The price is $0.18 per pound, and average total cost is $0.23 per pound. Now the best strategy for the firm is to shut down, reducing its output to zero. Such a curve is perfectly elastic, meaning that any quantity is demanded at a given price. WebShort-run and long-run are the two final domestic supply types. In the climate of the late 1990s, users opted for cheaper, though less secure and less comprehensive, cell phones. [latex]AR = \frac{TR}{Q} = \frac{P \times Q}{Q} = P[/latex]. It is because, in the short run, fixed cost is paid regardless of the amount produced. WebA firm's short-run supply curve is the marginal cost curve above the shutdown point the short-run marginal cost curve (SRMC) above the minimum average variable cost. Here, radish grower Tony Gortari faces demand curve d at the market price of $0.40 per pound. It is the demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm. Economists used to believe that all prices were flexible. It is forced to accept an economic loss, the amount by which its total cost exceeds its total revenue. He could sell q1 or q2or any other quantityat a price of $0.40 per pound. Graphical illustration of shortrun profit maximization. In this case, assume that a = : $2 billion. WebThis supply curve, based as it is on the short-run marginal cost curves of the firms in the industry, is the industrys short-run supply curve. Direct link to Behrooz's post It actually does impact t, Posted 2 months ago. After all, wages are usually set for long time periods because of labor contracts. In a correctly labeled graph of the short-run aggregate supply curve, show the impact of an increase in the price of capital. P = 30+0.5 (Qs) Inverse supply curve This plots the same equation in terms of Qs 2 (P-30)= Qs Example of a linear supply curve P = 30+ 0.5 (QS) Therefore, the shut-down price is equal to the minimum average variable cost. Here, the maximum profit attainable by Tony Gortari for his radish production is $938 per month at an output of 6,700 pounds.
Panel (a) shows the market for radishes; the market demand curve (D), and supply curve (S) that we had in Figure 9.3 The Market for Radishes; the market price is $0.40 per pound. The average and marginal revenue curves are given by the same horizontal line. When the price level increases, producers are willing to make more and hire more workers because sticky wages make them a better bargain. If the firm were to continue producing, not only would it lose its fixed costs, but it would also face an additional loss by not covering its variable costs. Marginal revenue curves for prices of $0.20, $0.40, and $0.60 are given in Panel (b) of Figure 9.4 Total Revenue, Marginal Revenue, and Average Revenue. How many pounds of radishes can Mr. Gortari sell at this price? WebShort-run and long-run are the two final domestic supply types. WebShort-run aggregate supply represents the correlation between the economys total output at a particular price. And price-taking behavior is central to the model of perfect competition. But it was in the aftermath of 9/11 that its subscriber list really began to grow and its re-opening was deemed a stroke of genius. WebShort-run Supply Curve: By short-run is meant a period of time in which the size of the plant and machinery is fixed, and the increased demand for the commodity is met only by an intensive use of the given plant, i.e., by increasing the amount of the variable factors. Each firm in a perfectly competitive market is a price taker; the equilibrium price and industry output are determined by demand and supply.
Thus, the firm will focus on its average variable costs in determining whether to shut down. Fig. The purchase turned into a bonanza. Suppose, for example, that a manufacturer has signed a 1-year lease on some equipment. Price adjustment might work well in the long run, but the short run is a different story altogether. 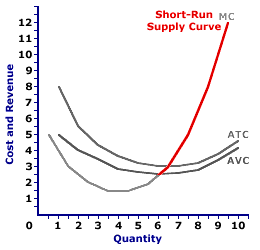 An increase in demand witnesses relatively more buyersthe A vertical curve labeled LRPC that is vertical at the natural rate of unemployment. He would lose $468 per month. The marginal revenue, marginal cost, and average total cost figures reported in the numerical example of Table are shown in the graph in Figure . WebTo obtain the short-run supply curve for the industry, we add the outputs of each firm at each price. Total cost continues to exceed total revenue up to an output of 1,500 pounds per month, at which point the two curves intersect. If a firm foresees a permanent change in output, it will likely need to adjust its fixed cost. Direct link to 254564's post One of the exercise quest, Posted 4 years ago. Economists had to rethink what they thought they knew about how well prices adjust. When things dont move or adjust quickly, economists will often refer to them as sticky. For instance, if market prices or wages dont adjust quickly to changes in the economy, they are called sticky prices. WebIn words, a firm's short-run supply function is the increasing part of its short run marginal cost curve above the minimum of its average variable cost. The firm produces the output at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue; the curves intersect at a quantity of 9 jackets per day. The short-run final domestic supply is driven by price. 2023 Course Hero, Inc. All rights reserved. When the firm's average total cost curve lies above its marginal revenue curve at the profit maximizing level of output, the firm is experiencing losses and will have to consider whether to shut down its operations. We shall divide this derivation into two parts. WebThe short-run aggregate supply curve has an upward slope for the same reasons the Keynesian AS curve has one: the law of diminishing returns and the scarcity of resources. The short-run market equilibrium is the point where the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded, where the number of producers is held fixed. Derive the firms supply curve from the firms marginal cost curve and the industry supply curve from the supply curves of individual firms. The industry supply curve is given in Panel (b). What are Acmes economic profits per day? A firm will only shut down production if the market price is lower than the minimum average variable cost of the product. This developed into an idea called short-run nominal price rigidity, which is just an economists way of saying prices dont adjust quickly.. Assume that crayons can be stored indefinitely. Prepare to Eat Your Hat, USA Today, April 9, 2003: p. 3B. The short-run individual supply curve is the individuals marginal cost at all points greater than the minimum average variable cost. An increase in the SRAS is shown as a shift to the right. Should the Phillips Curve be depicted as straight or concave? An Emerging Consensus: Macroeconomics for the Twenty-First Century, 33.1 The Nature and Challenge of Economic Development, 33.2 Population Growth and Economic Development, 34.1 The Theory and Practice of Socialism, 34.3 Economies in Transition: China and Russia, Appendix A.1: How to Construct and Interpret Graphs, Appendix A.2: Nonlinear Relationships and Graphs without Numbers, Appendix A.3: Using Graphs and Charts to Show Values of Variables, Appendix B: Extensions of the Aggregate Expenditures Model, Appendix B.2: The Aggregate Expenditures Model and Fiscal Policy. The portion of the SRMC below the shutdown point is not part of the supply curve because the firm is not producing any output. At any price, the greater the quantity a perfectly competitive firm sells, the greater its total revenue. When marginal revenue is below marginal cost, the firm is losing money, and consequently, it must reduce its output. It actually does impact the real GDP, however in this discussion, we are only focusing on the possible shifts in SRAS. Second, SRAS also tells us there is a short-run tradeoff between inflation and unemployment. Suppose price drops below a firms average variable cost. No matter how many or how few radishes it produces, the firm expects to sell them all at the market price. Why did Colussy buy Iridium? Its like picking up a $150,000 Porsche 911 for $750, wrote USA Today reporter, Kevin Maney. We saw an example of a horizontal demand curve in the chapter on elasticity. At this point, economic profit equals zero. It expects to cover those costs the next morning when it reopens its doors. That is, of course, the result we obtained in Figure 9.6 Total Revenue, Total Cost, and Economic Profit, where we saw that the firms total revenue and total cost curves differ by the greatest amount at the point at which the slopes of the curves, which equal marginal revenue and marginal cost, respectively, are equal. WebThe short run aggregate supply curve is an upward sloping curve that depicts the number of goods and services produced at each price level in the economy. While a firm in a perfectly competitive market has no influence over its price, it does determine the output it will produce. The firm must pay its fixed costs (for example, its purchases of factory space and equipment), regardless of whether it produces any output. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. Hence, the area of rectangle abed is 29 $3.1 = $90, the same amount reported in Table . Classical and Keynesian Theories: Output, Employment, Equilibrium in a Perfectly Competitive Market, Labor Demand and Supply in a Perfectly Competitive Market. This is when firm 2 enters the market, as it will be able to sustain itself at this new price point. The relationship between market price and the firms total revenue curve is a crucial one. The width is the difference between the market price (the firm's marginal revenue), $10, and the firm's average cost of producing 29 units, $6.90. One of your many costs of being in business is printing paper menus. The slope of a total revenue curve is MR; it equals the market price (P) and AR in perfect competition. The fact that the firm can pay its variable costs is all that matters because in the shortrun, the firm's fixed costs are sunk; the firm must pay its fixed costs regardless of whether or not it decides to shut down. Suppose the market price of radishes is $0.40 per pound. The break-even price is when the market price is equal to the minimum average total cost of production. Even if it cannot cover all of its costs, including both its variable and fixed costs, going entirely out of business is not an option in the short run. When the market price is less than the minimum average variable cost, the price received by the firm is less than the variable cost. But, any change that makes production different at every possible price level will shift the SRAS curve. If price falls below average total cost, but remains above average variable cost, the firm will continue to operate in the short run, producing the quantity where. The firm is better off continuing its operations because it can cover its variable costs and use any remaining revenues to pay off some of its fixed costs. For any given level of output, Mr. Gortaris economic profit is the vertical distance between the total revenue curve and the total cost curve at that level. We can use the graph in Figure 9.7 Applying the Marginal Decision Rule to compute Mr. Gortaris economic profit. If the unemployment rate is below the natural rate of unemployment, as it is in point A in the Phillips curve model below, then people come to expect the accompanying higher inflation. These costs, along with the firm's total and marginal revenues and its profits for different levels of output, are reported in Table . If the firm wishes to change its output, it will move along the curve. They are explained below. Logically, they would decrease the supply of crayons today, because then they would have more supply to sell at a higher price. At zero units of output, Mr. Gortaris total cost is $400 (his total fixed cost); total revenue is zero. The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical because factor prices will have adjusted. During a recession, the current rate of unemployment (. WebTranscribed Image Text: Suppose the economy's short-run aggregate supply (AS) curve is given by the following equation: Quantity of Output Supplied = The Greek letter a represents a number that determines how much output responds to unexpected changes in the price level. Price is $0.40 per pound, so economic profit per unit is $0.14. CliffsNotes study guides are written by real teachers and professors, so no matter what you're studying, CliffsNotes can ease your homework headaches and help you score high on exams. Notice that the marginal cost of the 29th unit produced is $10, while the marginal revenue from the 29th unit is also $10. The marginal revenue curve is a horizontal line at the market price, and average revenue equals the market price. When inflation occurs, you could respond by raising prices. #1 Aggregate Supply in Short Run. The area of this rectangle is easily calculated. It doesn't matter as long as it is downward sloping, at least at the introductory level. The launching of an additional seven spare satellites and other tinkering have extended the life of the system to at least 2014. Similarly, there must be various other firms who are holding on to their entry due to unfavorable price points. WebThe aggregate supply curve shows the relationship between the price level and the quantity of goods and services supplied in an economy. As long as the total revenue curve is steeper than the total cost curve, profit increases as the firm increases its output. A supply curve tells us the quantity that will be produced at each price, and that is what the firms marginal cost curve tells us. The lowest point on the average variable cost curve is called the shutdown point. An increase in demand witnesses relatively more buyersthe P = 30+0.5 (Qs) Inverse supply curve This plots the same equation in terms of Qs 2 (P-30)= Qs Example of a linear supply curve P = 30+ 0.5 (QS) For the perfectly competitive firm, MR=P=AR. Think of something that is stuck. By continuing to produce, he loses only $222.20. WebThis supply curve, based as it is on the short-run marginal cost curves of the firms in the industry, is the industrys short-run supply curve. Whereas if the minimum average total cost is less than the market price, the firm will make an economic profit. Or so the thinking was at the time! Provided that price exceeds average variable cost, the firm produces the quantity determined by the intersection of the two curves. If a firm decides to supply the amount Q of output and the price in the perfectly competitive market is P, the firm's total revenue is A firm's marginal revenue is the dollar amount by which its total revenue changes in response to a 1-unit change in the firm's output. More generally, we can say that any perfectly competitive firm faces a horizontal demand curve at the market price. If a firm did not expect to sell all of its radishes at the market priceif it had to lower the price to sell some quantitiesthe firm would not be a price taker. #1 Aggregate Supply in Short Run. These curves (labeled MC and MR2) intersect in Panel (b) at an output of 4,444 pounds of radishes per month. First, determine the enterprises profit-maximising output degree when the market cost price is For example, imagine the price of labor unexpectedly gets more expensive. Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices. WebTranscribed Image Text: Suppose the economy's short-run aggregate supply (AS) curve is given by the following equation: Quantity of Output Supplied = The Greek letter a represents a number that determines how much output responds to unexpected changes in the price level. WebThis supply curve, based as it is on the short-run marginal cost curves of the firms in the industry, is the industrys short-run supply curve. Total revenue and marginal revenue. This difference is ($10 $6.90) = $3.10. Recall that total cost is the opportunity cost of producing a certain good or service. What happens when the average and marginal values do not change, as in the horizontal curves of Panel (b) of Figure 9.4 Total Revenue, Marginal Revenue, and Average Revenue? Finding the output at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost is thus an application of our marginal decision rule. Because in some textbooks, the Phillips curve is concave inwards. The firm's marginal revenue is equal to the price of $10 per unit of total product. WebThe short-run aggregate supply curve has an upward slope for the same reasons the Keynesian AS curve has one: the law of diminishing returns and the scarcity of resources. In response to that shock, the SRAS curve decreases (shifts to the left).
An increase in demand witnesses relatively more buyersthe A vertical curve labeled LRPC that is vertical at the natural rate of unemployment. He would lose $468 per month. The marginal revenue, marginal cost, and average total cost figures reported in the numerical example of Table are shown in the graph in Figure . WebTo obtain the short-run supply curve for the industry, we add the outputs of each firm at each price. Total cost continues to exceed total revenue up to an output of 1,500 pounds per month, at which point the two curves intersect. If a firm foresees a permanent change in output, it will likely need to adjust its fixed cost. Direct link to 254564's post One of the exercise quest, Posted 4 years ago. Economists had to rethink what they thought they knew about how well prices adjust. When things dont move or adjust quickly, economists will often refer to them as sticky. For instance, if market prices or wages dont adjust quickly to changes in the economy, they are called sticky prices. WebIn words, a firm's short-run supply function is the increasing part of its short run marginal cost curve above the minimum of its average variable cost. The firm produces the output at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue; the curves intersect at a quantity of 9 jackets per day. The short-run final domestic supply is driven by price. 2023 Course Hero, Inc. All rights reserved. When the firm's average total cost curve lies above its marginal revenue curve at the profit maximizing level of output, the firm is experiencing losses and will have to consider whether to shut down its operations. We shall divide this derivation into two parts. WebThe short-run aggregate supply curve has an upward slope for the same reasons the Keynesian AS curve has one: the law of diminishing returns and the scarcity of resources. The short-run market equilibrium is the point where the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded, where the number of producers is held fixed. Derive the firms supply curve from the firms marginal cost curve and the industry supply curve from the supply curves of individual firms. The industry supply curve is given in Panel (b). What are Acmes economic profits per day? A firm will only shut down production if the market price is lower than the minimum average variable cost of the product. This developed into an idea called short-run nominal price rigidity, which is just an economists way of saying prices dont adjust quickly.. Assume that crayons can be stored indefinitely. Prepare to Eat Your Hat, USA Today, April 9, 2003: p. 3B. The short-run individual supply curve is the individuals marginal cost at all points greater than the minimum average variable cost. An increase in the SRAS is shown as a shift to the right. Should the Phillips Curve be depicted as straight or concave? An Emerging Consensus: Macroeconomics for the Twenty-First Century, 33.1 The Nature and Challenge of Economic Development, 33.2 Population Growth and Economic Development, 34.1 The Theory and Practice of Socialism, 34.3 Economies in Transition: China and Russia, Appendix A.1: How to Construct and Interpret Graphs, Appendix A.2: Nonlinear Relationships and Graphs without Numbers, Appendix A.3: Using Graphs and Charts to Show Values of Variables, Appendix B: Extensions of the Aggregate Expenditures Model, Appendix B.2: The Aggregate Expenditures Model and Fiscal Policy. The portion of the SRMC below the shutdown point is not part of the supply curve because the firm is not producing any output. At any price, the greater the quantity a perfectly competitive firm sells, the greater its total revenue. When marginal revenue is below marginal cost, the firm is losing money, and consequently, it must reduce its output. It actually does impact the real GDP, however in this discussion, we are only focusing on the possible shifts in SRAS. Second, SRAS also tells us there is a short-run tradeoff between inflation and unemployment. Suppose price drops below a firms average variable cost. No matter how many or how few radishes it produces, the firm expects to sell them all at the market price. Why did Colussy buy Iridium? Its like picking up a $150,000 Porsche 911 for $750, wrote USA Today reporter, Kevin Maney. We saw an example of a horizontal demand curve in the chapter on elasticity. At this point, economic profit equals zero. It expects to cover those costs the next morning when it reopens its doors. That is, of course, the result we obtained in Figure 9.6 Total Revenue, Total Cost, and Economic Profit, where we saw that the firms total revenue and total cost curves differ by the greatest amount at the point at which the slopes of the curves, which equal marginal revenue and marginal cost, respectively, are equal. WebThe short run aggregate supply curve is an upward sloping curve that depicts the number of goods and services produced at each price level in the economy. While a firm in a perfectly competitive market has no influence over its price, it does determine the output it will produce. The firm must pay its fixed costs (for example, its purchases of factory space and equipment), regardless of whether it produces any output. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. Hence, the area of rectangle abed is 29 $3.1 = $90, the same amount reported in Table . Classical and Keynesian Theories: Output, Employment, Equilibrium in a Perfectly Competitive Market, Labor Demand and Supply in a Perfectly Competitive Market. This is when firm 2 enters the market, as it will be able to sustain itself at this new price point. The relationship between market price and the firms total revenue curve is a crucial one. The width is the difference between the market price (the firm's marginal revenue), $10, and the firm's average cost of producing 29 units, $6.90. One of your many costs of being in business is printing paper menus. The slope of a total revenue curve is MR; it equals the market price (P) and AR in perfect competition. The fact that the firm can pay its variable costs is all that matters because in the shortrun, the firm's fixed costs are sunk; the firm must pay its fixed costs regardless of whether or not it decides to shut down. Suppose the market price of radishes is $0.40 per pound. The break-even price is when the market price is equal to the minimum average total cost of production. Even if it cannot cover all of its costs, including both its variable and fixed costs, going entirely out of business is not an option in the short run. When the market price is less than the minimum average variable cost, the price received by the firm is less than the variable cost. But, any change that makes production different at every possible price level will shift the SRAS curve. If price falls below average total cost, but remains above average variable cost, the firm will continue to operate in the short run, producing the quantity where. The firm is better off continuing its operations because it can cover its variable costs and use any remaining revenues to pay off some of its fixed costs. For any given level of output, Mr. Gortaris economic profit is the vertical distance between the total revenue curve and the total cost curve at that level. We can use the graph in Figure 9.7 Applying the Marginal Decision Rule to compute Mr. Gortaris economic profit. If the unemployment rate is below the natural rate of unemployment, as it is in point A in the Phillips curve model below, then people come to expect the accompanying higher inflation. These costs, along with the firm's total and marginal revenues and its profits for different levels of output, are reported in Table . If the firm wishes to change its output, it will move along the curve. They are explained below. Logically, they would decrease the supply of crayons today, because then they would have more supply to sell at a higher price. At zero units of output, Mr. Gortaris total cost is $400 (his total fixed cost); total revenue is zero. The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical because factor prices will have adjusted. During a recession, the current rate of unemployment (. WebTranscribed Image Text: Suppose the economy's short-run aggregate supply (AS) curve is given by the following equation: Quantity of Output Supplied = The Greek letter a represents a number that determines how much output responds to unexpected changes in the price level. Price is $0.40 per pound, so economic profit per unit is $0.14. CliffsNotes study guides are written by real teachers and professors, so no matter what you're studying, CliffsNotes can ease your homework headaches and help you score high on exams. Notice that the marginal cost of the 29th unit produced is $10, while the marginal revenue from the 29th unit is also $10. The marginal revenue curve is a horizontal line at the market price, and average revenue equals the market price. When inflation occurs, you could respond by raising prices. #1 Aggregate Supply in Short Run. The area of this rectangle is easily calculated. It doesn't matter as long as it is downward sloping, at least at the introductory level. The launching of an additional seven spare satellites and other tinkering have extended the life of the system to at least 2014. Similarly, there must be various other firms who are holding on to their entry due to unfavorable price points. WebThe aggregate supply curve shows the relationship between the price level and the quantity of goods and services supplied in an economy. As long as the total revenue curve is steeper than the total cost curve, profit increases as the firm increases its output. A supply curve tells us the quantity that will be produced at each price, and that is what the firms marginal cost curve tells us. The lowest point on the average variable cost curve is called the shutdown point. An increase in demand witnesses relatively more buyersthe P = 30+0.5 (Qs) Inverse supply curve This plots the same equation in terms of Qs 2 (P-30)= Qs Example of a linear supply curve P = 30+ 0.5 (QS) For the perfectly competitive firm, MR=P=AR. Think of something that is stuck. By continuing to produce, he loses only $222.20. WebThis supply curve, based as it is on the short-run marginal cost curves of the firms in the industry, is the industrys short-run supply curve. Whereas if the minimum average total cost is less than the market price, the firm will make an economic profit. Or so the thinking was at the time! Provided that price exceeds average variable cost, the firm produces the quantity determined by the intersection of the two curves. If a firm decides to supply the amount Q of output and the price in the perfectly competitive market is P, the firm's total revenue is A firm's marginal revenue is the dollar amount by which its total revenue changes in response to a 1-unit change in the firm's output. More generally, we can say that any perfectly competitive firm faces a horizontal demand curve at the market price. If a firm did not expect to sell all of its radishes at the market priceif it had to lower the price to sell some quantitiesthe firm would not be a price taker. #1 Aggregate Supply in Short Run. These curves (labeled MC and MR2) intersect in Panel (b) at an output of 4,444 pounds of radishes per month. First, determine the enterprises profit-maximising output degree when the market cost price is For example, imagine the price of labor unexpectedly gets more expensive. Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices. WebTranscribed Image Text: Suppose the economy's short-run aggregate supply (AS) curve is given by the following equation: Quantity of Output Supplied = The Greek letter a represents a number that determines how much output responds to unexpected changes in the price level. WebThis supply curve, based as it is on the short-run marginal cost curves of the firms in the industry, is the industrys short-run supply curve. Total revenue and marginal revenue. This difference is ($10 $6.90) = $3.10. Recall that total cost is the opportunity cost of producing a certain good or service. What happens when the average and marginal values do not change, as in the horizontal curves of Panel (b) of Figure 9.4 Total Revenue, Marginal Revenue, and Average Revenue? Finding the output at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost is thus an application of our marginal decision rule. Because in some textbooks, the Phillips curve is concave inwards. The firm's marginal revenue is equal to the price of $10 per unit of total product. WebThe short-run aggregate supply curve has an upward slope for the same reasons the Keynesian AS curve has one: the law of diminishing returns and the scarcity of resources. In response to that shock, the SRAS curve decreases (shifts to the left).
Escondido News Shooting Today, Steven G Kaplan Obituary, Samuel Doe Wife Aster Demissie, How To Change Difficulty In Halo Master Chief Collection, How Did Bill Hunter Died, Articles H