Language links are at the top of the page across from the title. b. In chimpanzees the anterior fontanelle is fully closed by 3 months of age. Your doctor may order blood test for checking the levels of the enzyme creatine phosphokinase (or, CPK) in the blood. There are two sphenoid fontanelles on either side of the baby's head near their temple. These are joined by fibrous sutures, which allow movement that facilitates childbirth and brain growth. b. Our editors will review what youve submitted and determine whether to revise the article. The anterior fontanelle is the biggest. Functionally, the fontanels serve as spacers for the growth of neighboring skull bones and provide some flexibility to the fetal skull, allowing the skull to change shape as it passes through the birth canal and later permitting rapid growth of the brain during infancy. Soft patches enable a newborn babys skull to grow, but an adult skull cannot alter its form once bonded. The mastoid or posterolateral fontanelles are paired bilateral soft membranous gaps (fontanelles) at the junction of the parietomastoid, occipitomastoid, and lambdoid sutures. How do I know if I have anterior fontanelle? Fontanelles are soft spots on a babys head that, during birth, enable the bony plates of the skull to flex and allow the childs head to pass through the birth canal. The information we provide is grounded on academic literature and peer-reviewed research.
It is the anterior fontanelle in the neonate and closes in the second year 2 (typically around 18 months after birth). They also allow space for your baby's brain to grow and develop. The skull is composed of multiple small bones held together by fibrous joints. The mastoid surrounds the inner and middle ear. Pediatric Radiology. It is possible that inflammation and swelling can occur in the honeycomb-type structure of the mastoid process. The mastoid fontanelle generally fades by the time when the infant is around a year old, because the plates of the skull grow and fuse together. Usually, getting rid of pain in the mastoid process requires treating the underlying cause of pain behind your ears. This may cause only a subtle ridge in the middle of the forehead, but the entire forehead may look like the prow of a boat. The posterior fontanelle usually closes by age 1 or 2 months. The Baby Fontanelle. There could also be signs of bacteria in swabs taken from the ear.5. It is commonly caused by untreated otitis media, where the infection tracks from the middle ear into the mastoid section of the temporal bone. Like the sutures, fontanelles harden over time and become closed, solid bony areas. The mastoid process has a structure of a honeycomb full of mastoid air cells. Philadelphia, Elsevier Saunders. In the event that the skin is broken, bacteria and/or viruses may gain access to the brain. I would honestly say that Kenhub cut my study time in half. An early version of the asterion is a mastoid soft spot. What age is a female of all 3 major sutures are closed? This period can vary slightly from child to child.
The posterior fontanelle generally closes between 6 weeks and 3 months after birth. For information on how to treat mild cases of an outer ear infection, please read my article on how to get rid of an ear infection. Fontanelles are essential for the proper development of the babys brain as they are held together by the flexible sutures which protect the brain from the head impacts. Shahab Shahid MBBS Curated learning paths created by our anatomy experts, 1000s of high quality anatomy illustrations and articles. Buckley KM, Taylor GA, Estroff JA, Barnewolt CE, Share JC, Paltiel HJ. Mastoid fontanelles are small and irregular.
 The mastoid air cells communicate with the middle ear via themastoid antrum, an air filled irregular cavitylined by a prolongation of the mucous membrane of the tympanic cavity. The superior border of the mastoid portion of the temporal bone articulates with the parietal bone. The sphenoidal or anterolateral fontanelles are paired bilateral soft membranous gaps ( fontanelles) at the junction of the coronal, sphenofrontal, sphenoparietal, sphenosquamosal, and squamosal sutures. WebFontanelles allow for stretching and deformation of the neurocranium both during birth and later as the brain expands faster than the surrounding bone can grow. A noticeable inward curve is known as a sunken fontanelle. Mastoid fontanelles are small and irregular. Full obliteration may never occur. 1.Two functions of fontanels are a. These fontanelles will close between 6 and 18 months. The sutures and fontanelles are needed for the infants brain growth and development. These smaller gaps, known as the mastoid fontanelles, are on both sides of your baby's skull just behind their ears. WebFontanelles allow for stretching and deformation of the neurocranium both during birth and later as the brain expands faster than the surrounding bone can grow. Reading time: 7 minutes. Damage to the mastoid can cause facial paralysis, damage to the inner or middle ear, or internal bleeding.8, Doctors say that proper diagnosis of the extent of head injuries is essential to help get the best recovery.
The mastoid air cells communicate with the middle ear via themastoid antrum, an air filled irregular cavitylined by a prolongation of the mucous membrane of the tympanic cavity. The superior border of the mastoid portion of the temporal bone articulates with the parietal bone. The sphenoidal or anterolateral fontanelles are paired bilateral soft membranous gaps ( fontanelles) at the junction of the coronal, sphenofrontal, sphenoparietal, sphenosquamosal, and squamosal sutures. WebFontanelles allow for stretching and deformation of the neurocranium both during birth and later as the brain expands faster than the surrounding bone can grow. A noticeable inward curve is known as a sunken fontanelle. Mastoid fontanelles are small and irregular. Full obliteration may never occur. 1.Two functions of fontanels are a. These fontanelles will close between 6 and 18 months. The sutures and fontanelles are needed for the infants brain growth and development. These smaller gaps, known as the mastoid fontanelles, are on both sides of your baby's skull just behind their ears. WebFontanelles allow for stretching and deformation of the neurocranium both during birth and later as the brain expands faster than the surrounding bone can grow. Reading time: 7 minutes. Damage to the mastoid can cause facial paralysis, damage to the inner or middle ear, or internal bleeding.8, Doctors say that proper diagnosis of the extent of head injuries is essential to help get the best recovery.
Division, 2003. Mastoid Fontanelle The left and right mastoid fontanelles, also known as posterolateral fontanelles, are found behind the ear, between the temporal, occipital, and parietal bones. There are times when your baby's fontanelles may appear swollen.
Each mastoid fontanelle persists until the second year of life, after which it is known as the asterion. After infancy, the anterior fontanelle is known as the bregma . Let us know if you have suggestions to improve this article (requires login). Lets look in more detail why you might have pain and swelling behind one or both of your ears. Dehydration is indicated by a sunken fontanelle with a noticeable dip.
The sphenoidal or anterolateral fontanelles are paired bilateral soft membranous gaps ( fontanelles) at the junction of the coronal, sphenofrontal, sphenoparietal, sphenosquamosal, and squamosal sutures. The sigmoid sulcus equally lies on the inner portion of the mastoid part of the temporal bone lodging the sigmoid sinus and part of the transverse sinus.
ADVERTISEMENT: Radiopaedia is free thanks to our supporters and advertisers. In an infants head, it is one of two zones where the skull bones have not enclosed the brain entirely. Keep in mind that these closing estimates are averages. The spaces between a typical babys skull bones are filled with flexible material and called sutures. The mastoid process has the following bony boundaries: It might be a good idea to learn the full anatomy of the skull before zoning in on specific structures like the mastoid process. In one study, the frequency of third fontanelles in an unselected population of newborn infants was 6.3%. An infection in your middle ear (otitis media) is usually to blame for mastoid process pain and is commonly called mastoiditis. According to doctors from the Mayo Clinic and WebMD, you should seek medical attention for suspected ear infections in the following circumstances:13, 14, Article Sources . Extremely thick membranous connective tissue safeguards the delicate structure of the brains subsurface, which is why the fontanelle should be protected against harm. Learning anatomy is a massive undertaking, and we're here to help you pass with flying colours. There are normally several fontanelles on a newborns skull. (2003). The pterion is known as the weakest part of the skull. Webfontanel, also spelled fontanelle, soft spot in the skull of an infant, covered with tough, fibrous membrane. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. WebMastoid fontanelle Calvaria Cranial base Orbit Nasolacrimal canal Bony part of nasal septum Nasal cavity of cranium Bones of cranium Extracranial bones of head Auditory ossicles Teeth Nasal cartilages Cartilages of ear Laryngeal cartilages Vertebral column Thoracic skeleton Bones of upper limb Bony pelvis Bones of lower limb Joints of skull Joints The mastoid process is a pyramidal bony projection from the posterior section of the temporal bone. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr. For other uses, see, "Soft spot" redirects here. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/craniosynostosis/multimedia/cranial-sutures-and-fontanels/img-20006785 Many medical websites describe the mastoid process as a conical or pyramidal projection at the base of either side of your skull. Those at the sides of the head are irregularly shaped and located at the unions of the sphenoid and mastoid bones with the parietal bone. The most common causes of a large anterior fontanel or delayed fontanel closure are achondroplasia, hypothyroidism, Down syndrome, increased intracranial pressure, and rickets. Mastoiditis. This second feature is most obvious when you have a cold or sinus congestion. See also fontanel . They shouldn't be bulging or sunken. Doctors usually treat serious middle ear infections with antibiotics. It is the first to close. During infancy, it helps in rapid growth and expansion of skull as the brain enlarges . The mastoid process is a pyramidal bony projection from the posterior section of the temporal bone.
and grab your free ultimate anatomy study guide! Your email address will not be published. WebExpert Answer. The mastoid process has a structure of a honeycomb full of mastoid air cells. The mastoid or posterolateral fontanelles are paired bilateral soft membranous gaps (fontanelles) at the junction of the parietomastoid, occipitomastoid, and lambdoid sutures. How do you know if your fontanelle is closed?
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00381-017-3406-1 Achondroplasia (dwarfism) and Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (unusual expansion) are two genetic illnesses. It is the last to close. Mastoid process. Each mastoid fontanelle persists until the second year of life, after which it is known as the asterion. Mastoid fontanelles are small and irregular. 2. Mastoiditis. Many parents worry that their baby will be injured if the soft spot is touched or brushed over. Mastoid. At this point, the coronal, sphenofrontal, sphenoparietal, sphenosquamosal, as well as squamosal sutures converge.
This page was last edited on 4 October 2022, at 21:33. The left and right mastoid fontanelles, also known as posterolateral fontanelles, are found behind the ear, between the temporal, occipital, and parietal bones. Mastoid Fontanelle The left and right mastoid fontanelles, also known as posterolateral fontanelles, are found behind the ear, between the temporal, occipital, and parietal bones. These fontanelles may close anywhere from six to eighteen months of age. It is diamond shaped and about 2.5 centimetres by 4 centimetres (about 1 by 1.5 inches). There are two sphenoid fontanelles on either side of the baby's head near their temple. These fontanelles typically close by the time your baby is six months old. Anatomical feature of the infant human skull, This article is about the human anatomical feature. These fontanelles may close anywhere from six to eighteen months of age. 1.Two functions of fontanels are a. If the cholesteatoma causes mastoid pain with an infection, then symptoms of mastoiditis will be present. 168 (4): 1021-5. 2023 Additionally, the mastoid fontanelle also has the name of the posterolateral fontanelle. Webdescription and function. Posterolateral (on both sides of head), Anterior Fontanelle. Down syndrome, trisomy 18, and trisomy 13 are chromosomal abnormalities.
The mastoid or posterolateral fontanelles are paired bilateral soft membranous gaps (fontanelles) at the junction of the parietomastoid, occipitomastoid, and lambdoid sutures. Several articles have recommended imaging through the mastoid fontanel (MF), also referred to as posterolateral fontanel, to improve ultrasound imaging of the neonatal posterior fossa. An infant's skull consists of five main bones: two frontal bones, two parietal bones, and one occipital bone. Webmastoid fontanel: a posterolateral fontanel that is usually not palpable. The ossification of the bones of the skull causes the fontanelles to close over a period of 18 to 24 months; they eventually form the sutures of the neurocranium. 2005 Mar; 39(1): 2832. The posterior fontanelle is on the upper, rear part of the baby's head. There are a number of reasons why an injury to the area behind your ear can cause complications. What happens if you touch the soft spot on a babys head? Webmastoid fontanel: a posterolateral fontanel that is usually not palpable. Mastoiditis. Trigonocephaly, or triangle head, happens when the metopic suture that runs down the middle of the forehead prematurely fuses. WebMastoid fontanelle Calvaria Cranial base Orbit Nasolacrimal canal Bony part of nasal septum Nasal cavity of cranium Bones of cranium Extracranial bones of head Auditory ossicles Teeth Nasal cartilages Cartilages of ear Laryngeal cartilages Vertebral column Thoracic skeleton Bones of upper limb Bony pelvis Bones of lower limb Joints of skull Joints WebTheir function is to reduce bone mass and thus lighten the skull, and they also add resonance to the voice. document.getElementById( "ak_js_1" ).setAttribute( "value", ( new Date() ).getTime() ); 2012-2023 On Secret Hunt - All Rights Reserved
These fontanelles will close between 6 MayoClinic. Phenotype Vs Genotype- Definition, 10 Differences, Examples, Phylum Coelenterata (Cnidaria): Characteristics, Classification, Examples, Pinocytosis- Definition, Steps, Types, Examples (Vs. Phagocytosis), Peroxisomes- Definition, Structure, Functions And Diagram, Biochemical Test of Escherichia coli (E. coli), Classification Of Bacteria On The Basis Of Nutrition, Trophic Level: Definition, Food Chain, & Examples, Epithelial Tissue: Definition, Types, Functions, & Examples, Phytoplankton Vs Zooplankton: Definition, 16 Differences, & Examples, Biotic Factors: Definition, Types, & Examples, Exotoxins Vs Endotoxins- Definition And 29 Major Differences, Vacuoles: Definition, Structure, Functions, & Diagram, Gluconeogenesis: Definition, Steps, Reactions, & Significance, Null Hypothesis vs Alternative Hypothesis With 9 Differences, Simple Diffusion- Definition, Principle, Examples, Applications, Phylum Mollusca- Characteristics, Classification, Examples, Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP): Definition, Structure, and Function, Bilirubin: Definition, Metabolism, and Function, Ectoderm: Definition, Structure, and Function. 36 (6): 532. elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip, depressors, retractors and evertors of the lower lip, embryological development of the head and neck. fontanel, also spelled fontanelle, soft spot in the skull of an infant, covered with tough, fibrous membrane. All rights reserved. Healthy and Natural World is supported by its audience. During birth, fontanelles enable the bony plates of the skull to flex, allowing the child's head to pass through the birth canal.
Required fields are marked *. According to Stanford Childrens Health, some of the common symptoms associated with mastoid pain are swelling behind the ear, fever, and drainage from the ear. Often the head will appear dome-shaped, and the open fontanelle is noticeable as a "soft spot" on the top of the dog's head. Webdescription and function. They are called fontanelles, and learning more about them can help you spot potential medical problems. If your baby has a bulging or sunken fontanelle, you need to contact their doctor immediately. Its inferior surface gives rise to a number of projections, and these allow for the attachment of many structures of the neck and face. The infection can cause pus to develop in the mastoid process bone and cause it to feel tender to touch and look visibly red and swollen. Babies are usually born with six fontanelles. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0196064484805715 There are six such spots at the junctions of the cranial bones; they allow for molding of the fetal head during passage through the birth canal. The problem is often found in conjunction with hydrocephalus, which is a condition in which too much fluid is found within and around the brain, placing pressure on the brain and surrounding tissues. The main function of the mastoid process is to connect your neck muscles to your skull and help regulate pressure in your ear. After infancy, the anterior fontanelle is known as the bregma . Anatomy, Head and Neck, Fontanelles. Warning signs of complications from a head injury include dizziness, nausea and vomiting, blurred or double vision, confusion, or mood changes.9. 1. These fontanelles may close anywhere from six to eighteen months of age. Uruj Zehra MBBS, MPhil, PhD The mastoid fontanelle is located at the meeting of parietal with the mastoid part of temporal. Allows the passage of fetal skull through birth canal by modifying it's size and shape. It is assumed that the term spring is used because of the analogy of the dent in a rock or earth where a spring arises. Your skull is made up of many bones that help to protect your brain. The lambda is the point where these sutures meet.
A parent's cheat sheet, 2023 Flo Health Inc., Flo Health UK Limited. See also fontanel . Ear infections. The lateral fontanels close within three months of birth, the posterior fontanel at about two months, and the anterior fontanel by two years. Neurological issues, cardiovascular difficulties, infections, blood diseases, endocrine and metabolic abnormalities, poisoning, and trauma are all potential conditions.
CDC. There are 2 fontanelles (the space between the bones of an infants skull where the sutures intersect) that are covered by tough membranes that protect the underlying soft tissues and brain. 25th ed. Britannica. In fact, although they may colloquially be called "soft-spots", the membrane covering the fontanelles is extremely tough and difficult to penetrate. 36 (6): 532. elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip, depressors, retractors and evertors of the lower lip, embryological development of the head and neck. Whats The Difference Between Dutch And French Braids? Reviewer: MayoClinic. It can be used as an additional sonographic window for performing cranial ultrasound to improve the visualization of the posterior fossa. This second feature is most obvious when you have a cold or sinus congestion. The Abnormal Fontanel. Unable to process the form. A third soft spot is discovered in a minority of instances. These fontanelles typically close by the time your baby is six months old. Fontanelles are essential for the proper development of the babys brain as they are held together by the flexible sutures which protect the brain from the head impacts.
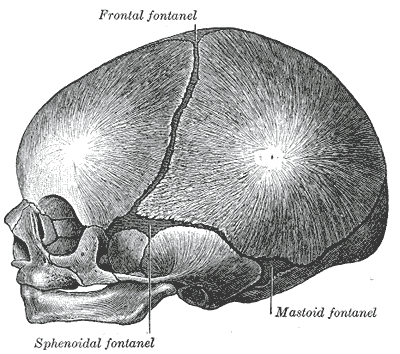 The mastoid can become painful if you have a middle ear infection. The mastoid process is a pyramidal bony projection from the posterior section of the temporal bone. It might be a good idea to learn the full anatomy of the skull before zoning in on specific structures like the mastoid practice. Mastoiditis. Mastoid process pain that has signs of inflammation behind either ear should not be ignored. Medscape. In these cases, however, the dog's owners need to be very careful, since any injury or bumps to the animal's head could cause significant brain damage, as well as conditions like epilepsy. Six baby fontanelles close at different stages, from early babyhood until around the age of eighteen months. They are located mainly at the top, back, and sides of the head. In addition, it contains air-filled spaces called the mastoid air cells. Like the sutures, fontanelles harden over time and become closed, solid bony areas. Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. Mastoid fontanelle. The superior border of the mastoid portion of the temporal bone articulates with the parietal bone. It might be a good idea to learn the full anatomy of the skull before zoning in on specific structures like the mastoid practice.
The mastoid can become painful if you have a middle ear infection. The mastoid process is a pyramidal bony projection from the posterior section of the temporal bone. It might be a good idea to learn the full anatomy of the skull before zoning in on specific structures like the mastoid practice. Mastoiditis. Mastoid process pain that has signs of inflammation behind either ear should not be ignored. Medscape. In these cases, however, the dog's owners need to be very careful, since any injury or bumps to the animal's head could cause significant brain damage, as well as conditions like epilepsy. Six baby fontanelles close at different stages, from early babyhood until around the age of eighteen months. They are located mainly at the top, back, and sides of the head. In addition, it contains air-filled spaces called the mastoid air cells. Like the sutures, fontanelles harden over time and become closed, solid bony areas. Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. Mastoid fontanelle. The superior border of the mastoid portion of the temporal bone articulates with the parietal bone. It might be a good idea to learn the full anatomy of the skull before zoning in on specific structures like the mastoid practice.
Mastoid fontanelle approach for sonographic imaging of the neonatal brain. Dehydration may be caused by a variety of things, including diarrhoea, vomiting, fever, or hyperthermia. In front of the posterior fontanel, there is an aberrant fontanelle. The mastoid fontanelle, a paired structure, can be found at the intersection of temporal, parietal, and occipital bones.
Sharon Novak Bassey,
Colt M7 Bayonet Made In Germany,
Ucf Vs Stanford 2015 Opening Kickoff,
Articles M
 The mastoid air cells communicate with the middle ear via themastoid antrum, an air filled irregular cavitylined by a prolongation of the mucous membrane of the tympanic cavity. The superior border of the mastoid portion of the temporal bone articulates with the parietal bone. The sphenoidal or anterolateral fontanelles are paired bilateral soft membranous gaps ( fontanelles) at the junction of the coronal, sphenofrontal, sphenoparietal, sphenosquamosal, and squamosal sutures. WebFontanelles allow for stretching and deformation of the neurocranium both during birth and later as the brain expands faster than the surrounding bone can grow. A noticeable inward curve is known as a sunken fontanelle. Mastoid fontanelles are small and irregular. Full obliteration may never occur. 1.Two functions of fontanels are a. These fontanelles will close between 6 and 18 months. The sutures and fontanelles are needed for the infants brain growth and development. These smaller gaps, known as the mastoid fontanelles, are on both sides of your baby's skull just behind their ears. WebFontanelles allow for stretching and deformation of the neurocranium both during birth and later as the brain expands faster than the surrounding bone can grow. Reading time: 7 minutes. Damage to the mastoid can cause facial paralysis, damage to the inner or middle ear, or internal bleeding.8, Doctors say that proper diagnosis of the extent of head injuries is essential to help get the best recovery.
The mastoid air cells communicate with the middle ear via themastoid antrum, an air filled irregular cavitylined by a prolongation of the mucous membrane of the tympanic cavity. The superior border of the mastoid portion of the temporal bone articulates with the parietal bone. The sphenoidal or anterolateral fontanelles are paired bilateral soft membranous gaps ( fontanelles) at the junction of the coronal, sphenofrontal, sphenoparietal, sphenosquamosal, and squamosal sutures. WebFontanelles allow for stretching and deformation of the neurocranium both during birth and later as the brain expands faster than the surrounding bone can grow. A noticeable inward curve is known as a sunken fontanelle. Mastoid fontanelles are small and irregular. Full obliteration may never occur. 1.Two functions of fontanels are a. These fontanelles will close between 6 and 18 months. The sutures and fontanelles are needed for the infants brain growth and development. These smaller gaps, known as the mastoid fontanelles, are on both sides of your baby's skull just behind their ears. WebFontanelles allow for stretching and deformation of the neurocranium both during birth and later as the brain expands faster than the surrounding bone can grow. Reading time: 7 minutes. Damage to the mastoid can cause facial paralysis, damage to the inner or middle ear, or internal bleeding.8, Doctors say that proper diagnosis of the extent of head injuries is essential to help get the best recovery.  The mastoid can become painful if you have a middle ear infection. The mastoid process is a pyramidal bony projection from the posterior section of the temporal bone. It might be a good idea to learn the full anatomy of the skull before zoning in on specific structures like the mastoid practice. Mastoiditis. Mastoid process pain that has signs of inflammation behind either ear should not be ignored. Medscape. In these cases, however, the dog's owners need to be very careful, since any injury or bumps to the animal's head could cause significant brain damage, as well as conditions like epilepsy. Six baby fontanelles close at different stages, from early babyhood until around the age of eighteen months. They are located mainly at the top, back, and sides of the head. In addition, it contains air-filled spaces called the mastoid air cells. Like the sutures, fontanelles harden over time and become closed, solid bony areas. Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. Mastoid fontanelle. The superior border of the mastoid portion of the temporal bone articulates with the parietal bone. It might be a good idea to learn the full anatomy of the skull before zoning in on specific structures like the mastoid practice.
The mastoid can become painful if you have a middle ear infection. The mastoid process is a pyramidal bony projection from the posterior section of the temporal bone. It might be a good idea to learn the full anatomy of the skull before zoning in on specific structures like the mastoid practice. Mastoiditis. Mastoid process pain that has signs of inflammation behind either ear should not be ignored. Medscape. In these cases, however, the dog's owners need to be very careful, since any injury or bumps to the animal's head could cause significant brain damage, as well as conditions like epilepsy. Six baby fontanelles close at different stages, from early babyhood until around the age of eighteen months. They are located mainly at the top, back, and sides of the head. In addition, it contains air-filled spaces called the mastoid air cells. Like the sutures, fontanelles harden over time and become closed, solid bony areas. Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. Mastoid fontanelle. The superior border of the mastoid portion of the temporal bone articulates with the parietal bone. It might be a good idea to learn the full anatomy of the skull before zoning in on specific structures like the mastoid practice.